Back to LING 385
Lecture 4
A little Linear Algebra
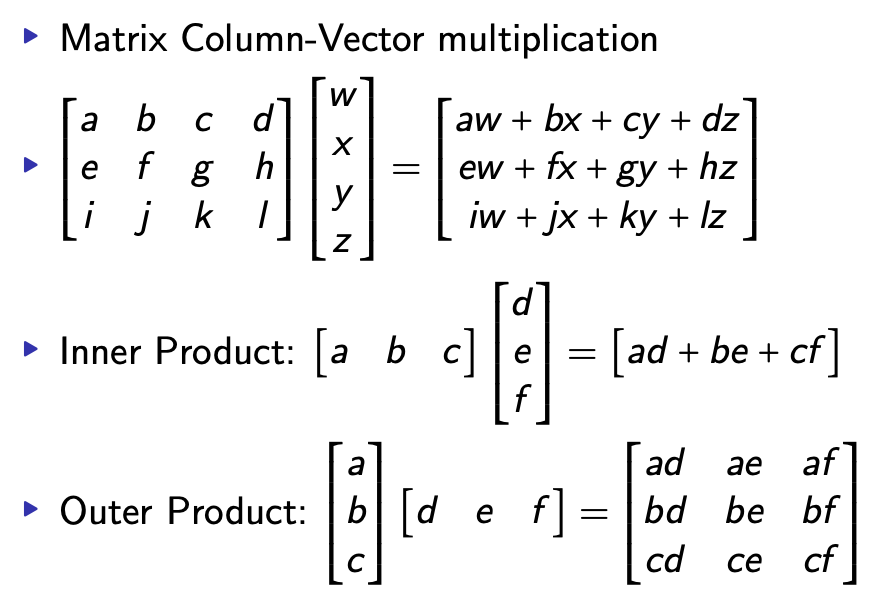
- inner product: row vector * column vector = scalar
- outer product: column vector * row vector = matrix
Learning and Recall of many patterns
- we start with many patterns of the same length
- calculate the "weight matrix" of each pattern (column * row)
- take the average of the matrices
- this is the entire memory bank
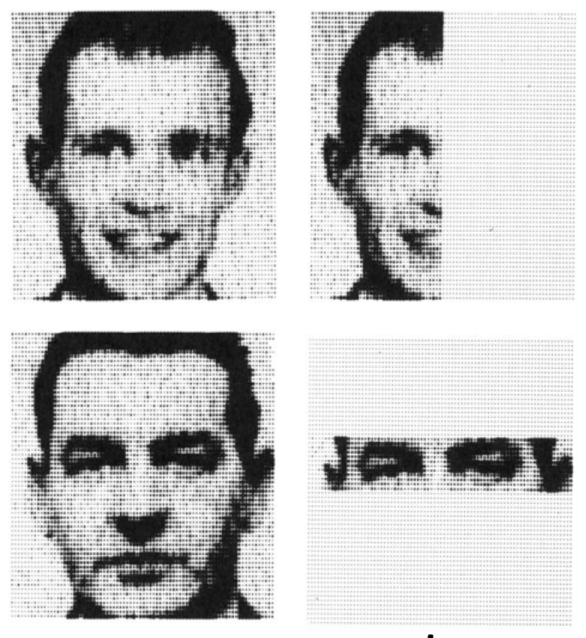
- reproduced by Kohonen in 1973 to create a face recognition network
- noisy/partial input → full output

Neurobiology
- Cajal: The brain is made of neurons! Neurons are electrically active.
- Adrian: Neurons are on or off
- Sherrington: Neurons can excite or inhibit other neurons at the synapse. Each neuron can be affected by all neurons connected to it.
- synapse = gap between neurons
- neuron integrates (adds up) activations of all the neurons that influence it
Learning
- how can we learn to associate a sound and visual appearance of one object?
- neurons sensitive to the sound are active when neurons sensitive to the color/shape are also active
- “Neurons that are active together, wire together”
- synapse between two neurons that are co-active changes to make the transmission between these two neurons more efficient
- this is Hebbian learning
Hopfield model of Hebbian Learning
- take the averages of each memory vector
- this is the "correlation memory matrix"
- each number in the matrix represents the activations between neurons
